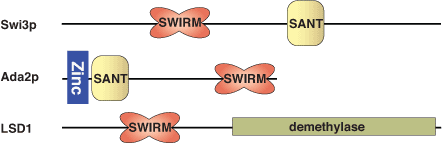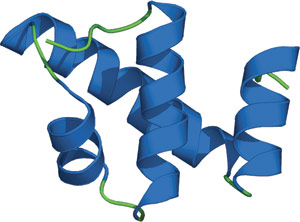
Structure of the SWIRM domain of the transcriptional adaptor, ADA2.
SWIRM is an evolutionarily conserved, eukaryotic domain found in proteins implicated in chromatin remodeling and gene expression. It is composed of approximately 85 amino acids that form a five-helix-bundle and a histone-like fold consisting of two helix-turn-helix motifs positioned around a long, central helix. Variation in the orientation of the helix-turn-helix motifs relative to one another may account for differences in cellular function across SWIRM domains. The SWIRM domains of human ADA2α and SMARC2 can bind both nucleosomal and double-stranded DNA. The SWIRM domain of ADA2a colocalizes with lysine-acetylated histone H3 in the nucleus and enhances access to nucleosomal linker DNA bound by histone H1, which potentiates ACF remodeling activity.