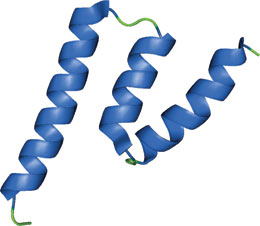
The GRIP domain of golgin-245.
The GRIP domain was originally identified as a conserved C-terminal domain present in a group of Golgi proteins isolated from yeast and mammals. GRIP domains interact with members of the Arf/Ar1 family of small GTPases, including Arl1 and Arl3. The GRIP domain structure consists of an S-shaped configuration of three helices with a concave and a convex face. The domain can form a head to tail homodimer that allows for Arl1-GTP protein interaction. Presence of this domain may be conserved within eukaryotic Golgi targeting pathways.
The structure shown is the crystal structure of the GRIP domain from golgin-245 in complex with Arl1-GTP, a member of the ARF/Arl small GTPase family. The interaction is predominantly mediated through hydrophobic interactions with the switch II region of Arl1. The GRIP domain also forms a tight homodimer where each subunit interacts independently with one Arl1-GTP; such dimerization appears to be required for GRIP domain-mediated Golgi targeting.
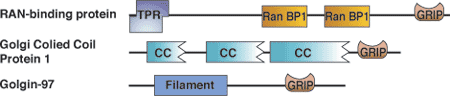
| GRIP domain proteins | Binding partners |
| Golgins | Arls |