Neuroinflammation is a condition observed in the central nervous system (CNS) in response to infection, toxic metabolites, traumatic injury, or autoimmunity. Immune cells, such as microglia, macrophages, and neuroepithelium-derived astrocytes, monitor synaptic homeostasis and facilitate the clearance of apoptotic cells in response to injury in the CNS to protect brain function.The immune system plays a significant role in shaping the brain during development and mediating damage, regeneration, and repair. These processes may be compromised in neurodegenerative diseases.
TREM2 is an immune receptor expressed on the cell surface of microglia, macrophages, osteoclasts, and immature dendritic cells. TREM2 forms a receptor-signaling complex with DAP12 to initiate cellular events like phagocytosis. TREM2 signaling is critical for the activation of microglia and may contribute to Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis by impairing microglia response, which leads to a buildup of β-amyloid.
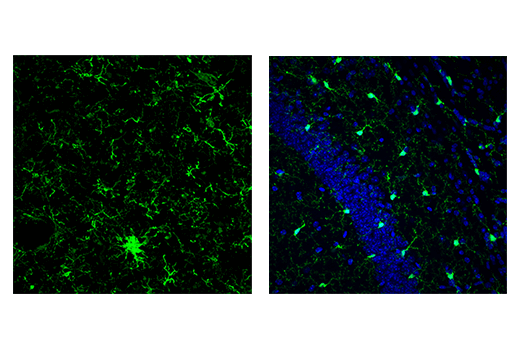
Iba1/AIF-1 is uniquely expressed in cells of monocytic lineage and is, therefore, widely used as a marker for microglia/macrophages in the brain and other tissue. Iba1/AIF-1 is an evolutionarily conserved calcium-binding protein containing a central pair of EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. Its function is not very well understood, but, as an F-actin-binding protein, Iba1/AIF-1 may function to remodel the actin cytoskeleton of microglia/macrophages.
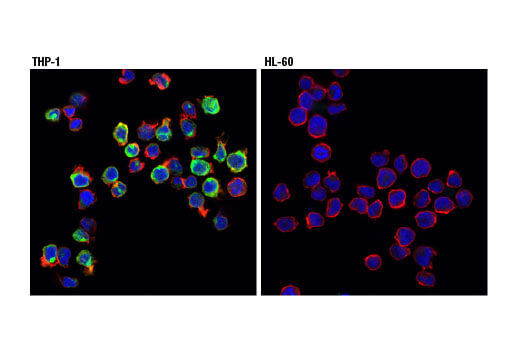
Cluster of differentiation molecule 11b (CD11b)/Integrin alpha M (ITGAM) is a transmembrane protein forming heterodimers that are composed of α and β subunits. CD11b/ITGAM is expressed by, and commonly used as a marker for, myeloid lineage cells such as neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, and microglia.
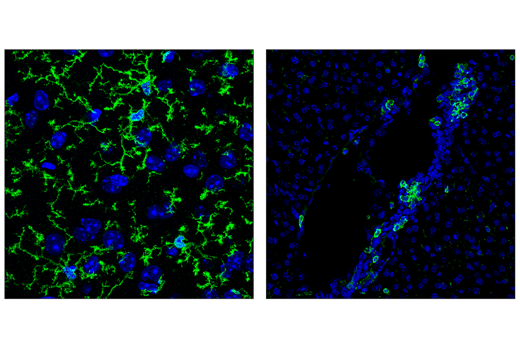
CD11c/ITGAX is a dendritic cell marker that forms a heterodimer with CD18. Transcriptional profiling of the brains from beta-amyloid mouse models revealed a TREM2-dependent increase in CD11c/ITGAX expression in microglia. Therefore, CD11c/ITGAX may serve as a marker of microglia associated with stage 2 disease. Changes in CD11c/ITGAX expression has also been observed in Huntington’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
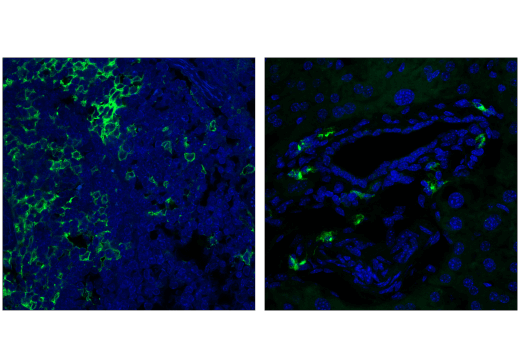
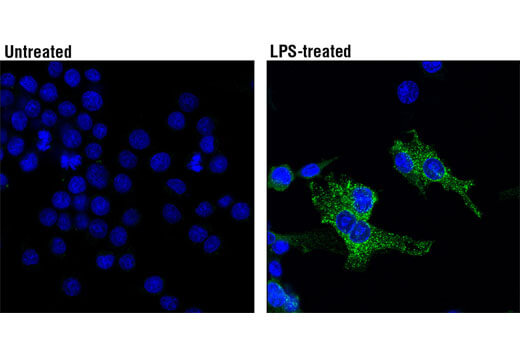
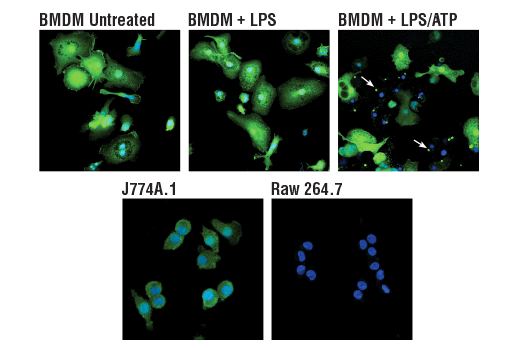
ASC/TMS1 is an adaptor protein that mediates formation of the inflammasome in response to tissue damage or infectious threats. Abnormal inflammasome activity may contribute to Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and Parkinson’s disease progression. In microglia, the NLRP3 inflammasome becomes activated when these cells sense proteins such as misfolded or aggregated beta-amyloid. ASC specks derived from microglia may also cross-seed beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Several other inflammasomes have been described in microglia and the other cells of the brain, including astrocytes and neurons, where their activation and subsequent caspase 1 cleavage contribute to disease development and progression.
Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression has been observed in brain glial cells and invading macrophages in response to injury. It is normally induced in an oxidative environment or in response to proinflammatory cytokines. iNOS has been linked with Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.